DevSecOps 101 part 1: Software Component Analysis (SCA)
Learn to detect/avoid vulnerable dependencies in app development with Software Composition Analysis (SCA) using a voluntary vulnerable Python app

I have been crawling through software engineering and cybersecurity blogs for a few years now, and I have always been surprised by the lack of cybersecurity resources targeting developers. Like if the cybersecurity and the developer community barely spoke to each other.
Our goal at Escape is to be a gap closer between those two worlds. Thus, I took this opportunity to write a full guide explaining how to secure an application during development. This guide targets CTOs, engineering leads, and developers. Therefore, it does not require any prior knowledge of cybersecurity.
To put it in practice, we will add a complete security testing to Damn Vulnerable Python Web Application throughout the whole guide. DVPWA, as its name tells, is a vulnerable web app written in Python. We will take Github Actions as an example of CI/CD, though this will be mostly generalizable.
You can find other parts of this guide below:
- Part 2: Detecting Insecure Source Code
- Part 3: Scanning Live Web Applications with Nuclei Scanner
- Part 4: Scanning Docker Images With Trivy
What is Software Component Analysis?
The first step towards building more secure apps is detecting and avoiding using dependencies that have known vulnerabilities. This process is called Software Component Analysis or SCA.
It involves breaking down the software into its constituent parts, such as modules, libraries, or classes, and analyzing their functionality, dependencies, interactions, and relationships. This analysis helps in identifying the building blocks of the software, understanding how they contribute to the system's behavior, and assessing their quality, performance, and reusability. Additionally, Software Component Analysis aids in managing dependencies, identifying potential risks, and facilitating effective software maintenance and evolution.
Security step 1: Detecting insecure dependencies
There are a few commercial options like Snyk SCA, but we will use the open-source pip package safety for this tutorial.
First, let's clone DVPWA, create a virtual environment, and install the dependencies.
git clone git@github.com:anxolerd/dvpwa.git
cd dvpwa
python3 -m virtualenv .venv && source .venv/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txtNow, let's install safety and run it
pip install safety
safety check --full-reportSimple, right? You should obtain the following output:
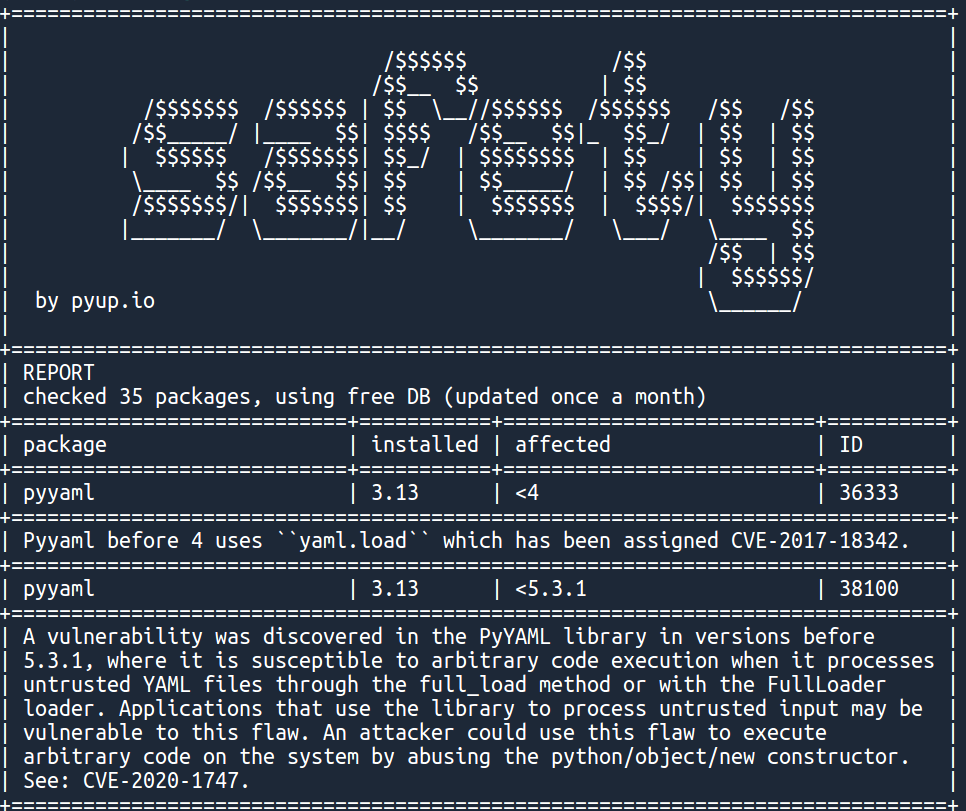
With several additional vulnerabilities. Notice that safety, as most SCA tools, gives information on the package version for which the vulnerability has been fixed. Good guy safety.
Now we know which of our packages are vulnerable, but what about triggering safety inside the CI/CD?
Integrating SCA into the CI/CD process
Let's add a Github workflow to our repository first. Create a: .github/workflows/main.yaml file and copy the following content inside:
on: [push]
jobs:
dependency_analysis:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
name: Test dependencies for security flaws
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name:
run: pip3 install safety && safety check
shell: bashAnd then commit it:
git add .github/ && git commit -m"Add safety SCA to CI"
git push origin masterClick on the actions tab of your dvpwa's repository on Github. You should see the following:
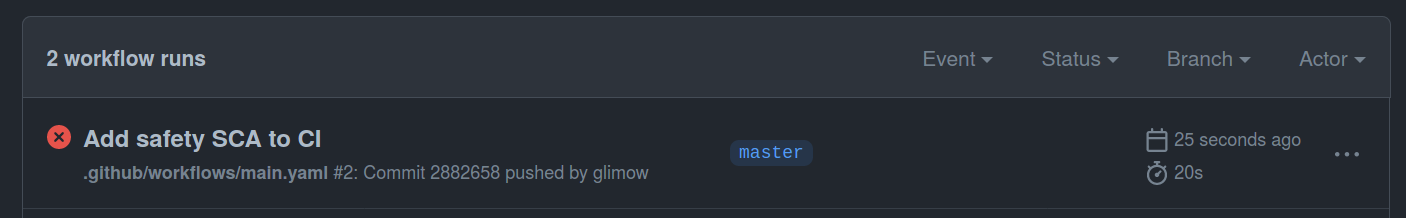
Notice that the action failed, which is perfectly normal since dvpwa uses a lot of insecure dependencies. Our Damn vulnerable app is less vulnerable now!
Conclusion
We added a first security step inside our CI/CD in just a few minutes! Of course, we focused on Python in this tutorial, but SCAs exist for most common languages, and most work similarly.
In the next tutorial, we will have a look at code analysis, aka programs that read your code, to find security flaws inside.
Automated security testing
Like performance and reliability, security is required to ship production-ready applications.
That's why at Escape, we created the first API Security scanner that allows developers to find and fix vulnerabilities in GraphQL applications during the development lifecycle before they even reach production!
It understands the business logic of APIs and looks for more than 70+ vulnerabilities so that you never have to worry again about
- Resolver performance (N+1 issues, cyclic queries, query complexity DOS…)
- Tenant isolation (access control, data segregation between users…)
- Sensitive data leaks (personally identifiable information, tokens, stack traces, secrets…)
- Injections (SQL, NoSQL, XSS…) and requests forgery
We constantly update our engine with state-of-the-art security research so that you never have to worry about the security of your applications again!
Get results in one minute!
