DAST vs Penetration Testing: Key Differences in 2026
Learn about the key differences between DAST and pentesting, the emerging role of AI pentesting, their roles in security testing, and which is right for your business.
The debate between DAST (Dynamic Application Security Testing) and penetration testing has evolved dramatically in the past few months. With more and more AI-powered solutions entering the market, organizations now face a more nuanced decision: not just when to choose DAST vs pentesting, but when to choose a modern AI DAST vs AI-driven automated pentesting.
Each serves a specific purpose. But understanding when to use which approach is essential for security teams trying to multiply their impact.
What is DAST?
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) scans running applications from the outside, identifying vulnerabilities without access to source code. Modern DAST is an automated security scanner that:
- Identifies common vulnerabilities (SQL injection, XSS, etc.) and business logic vulnerabilities that can be covered through single-step business logic security tests
- Built for engineering workflows: CI/CD integration, per-project RBAC, custom rules, and context-rich findings (screenshots, exploration graphs) so developers trust what they're fixing.
- Handles complex authentication scenarios
- Generates automated reports of findings
- Is a downstream multiplier: scanning results can flow into your security aggregation platforms like Wiz with enough context for proper risk prioritization
DAST tools excel at finding known vulnerability patterns at scale, making them valuable for continuous security testing in CI/CD pipelines.
What is Pentesting?
Penetration testing involves security experts manually testing applications to discover vulnerabilities. Traditional pentesting:
- Requires skilled security professionals
- Follows a structured methodology (reconnaissance, exploitation, reporting)
- Discovers business logic flaws and complex attack chains
- Provides detailed, contextualized findings
- Happens periodically (quarterly, annually)
- Delivers comprehensive written reports
The critical limitation? Traditional pentesting doesn't scale. In 2026, developers deploy every day, but penetration testing runs maybe 3-4 times a year and takes weeks to discover complex exploits, creating dangerous blind spots.
The idea of automating the pentesting process is not new, though. Automated pentesting tools have existed for years, trying to offer more frequent testing.
Overall, by automating web application penetration testing with the right tool, you can save up to 90% of the time compared to manual approaches. What typically takes 4 to 5 days can be reduced to just a few hours or minutes with automated tools. However, a lot of automated pentesting tools often struggle with false positives and cannot understand complex business logic. You have to know what to look into.
The Emerging Category: AI Pentesting
Over the last year, the security industry has been witnessing the emergence of AI-powered automated pentesting tools.
Most of the AI or Agentic pentesting tools leave the door open to a lot of promises. As with automated pentesting solutions, the quality of output will differ.
When we look at how pentesting is approached, essentially, it is not a tool. It’s a process. This is why it's important to consider the limitations of AI-native point pentesting solutions that focus mainly on exploitation:
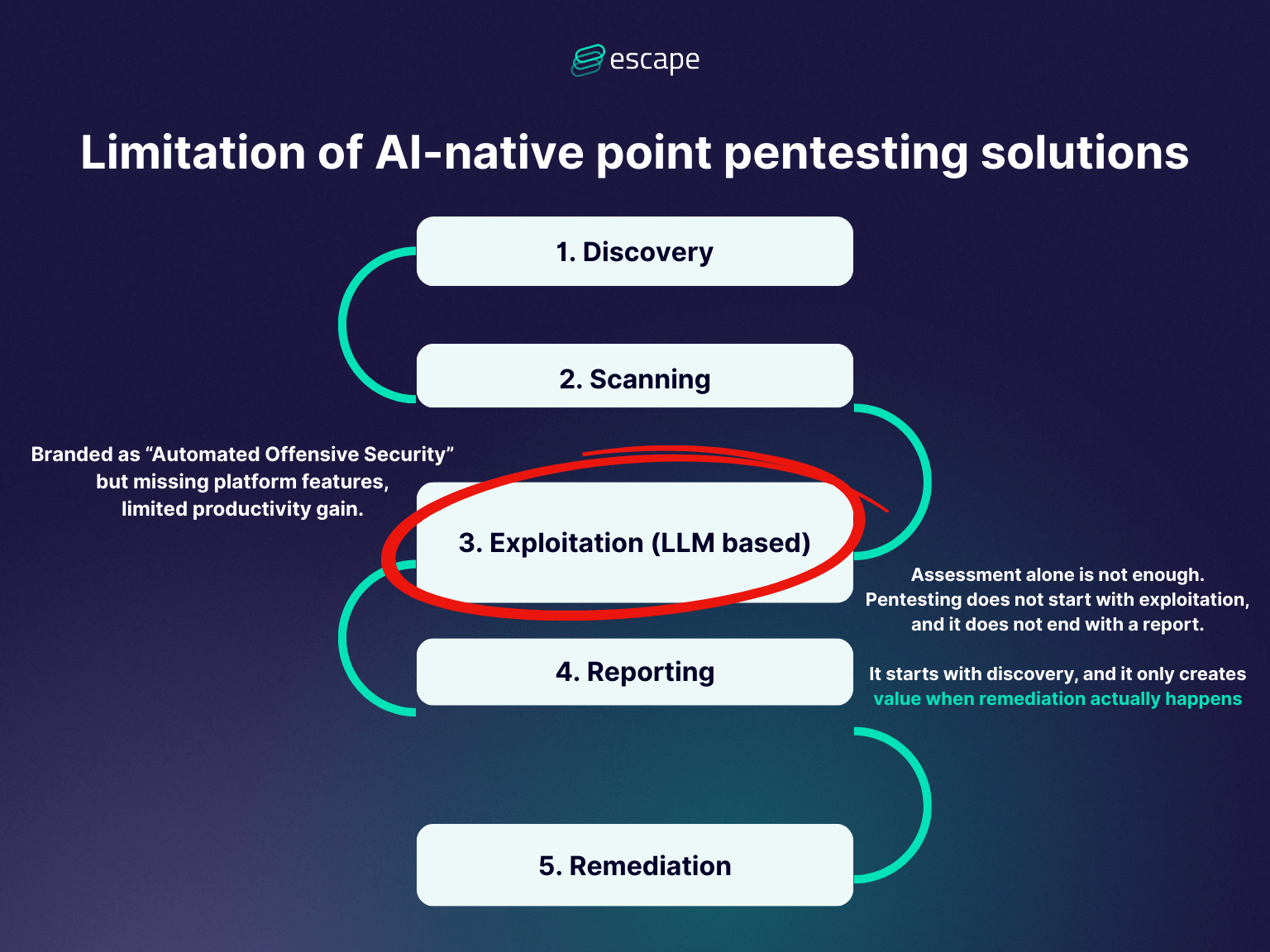
Pentesting does not start with exploitation, and it does not end with a report. The penetration testing process is usually carried out in 5 steps: Discovery, Scanning, Exploitation, Reporting, and Remediation.
It only creates value when remediation actually happens.
AI pentesting without process is just faster noise.
How Next-Generation DAST Enables AI Pentesting
At Escape, we've always communicating on how DAST should evolve from legacy solutions like Qualys DAST or Rapid7 DAST to modern approaches. Now, the evolution from modern DAST to AI-powered automated pentesting isn't about replacing DAST. Our goal was to build on top of a sophisticated DAST architecture to enable pentesting-level capabilities.
1. Graph-Based Knowledge Architecture: The DAST Foundation
Modern DAST has evolved beyond simple request-response scanning. Advanced solutions like Escape use in-house built graph-based approaches to:
- Map application structure - Understanding how APIs and web applications are interconnected
- Store business logic data - Capturing how your application actually works
- Track dependencies - Identifying relationships between requests and endpoints
- Focus on single assets - Building deep knowledge of individual applications
This graph-based DAST foundation enables something traditional scanners cannot: business logic security testing at scale.
With this architecture, DAST can run numerous single-step business logic tests that:
- Leverage customer environment data from the knowledge graph
- Understand request dependencies intelligently
- Test business logic scenarios that simple scanners miss
- Scale efficiently across your application portfolio
This is where traditional DAST ends.
And where AI pentesting begins.
2. From DAST to AI Pentesting: Adding the Attack Scenario Layer
When you take that sophisticated graph-based DAST architecture and combine it with real-time attack scenarios from the customer environment, you create something fundamentally different.
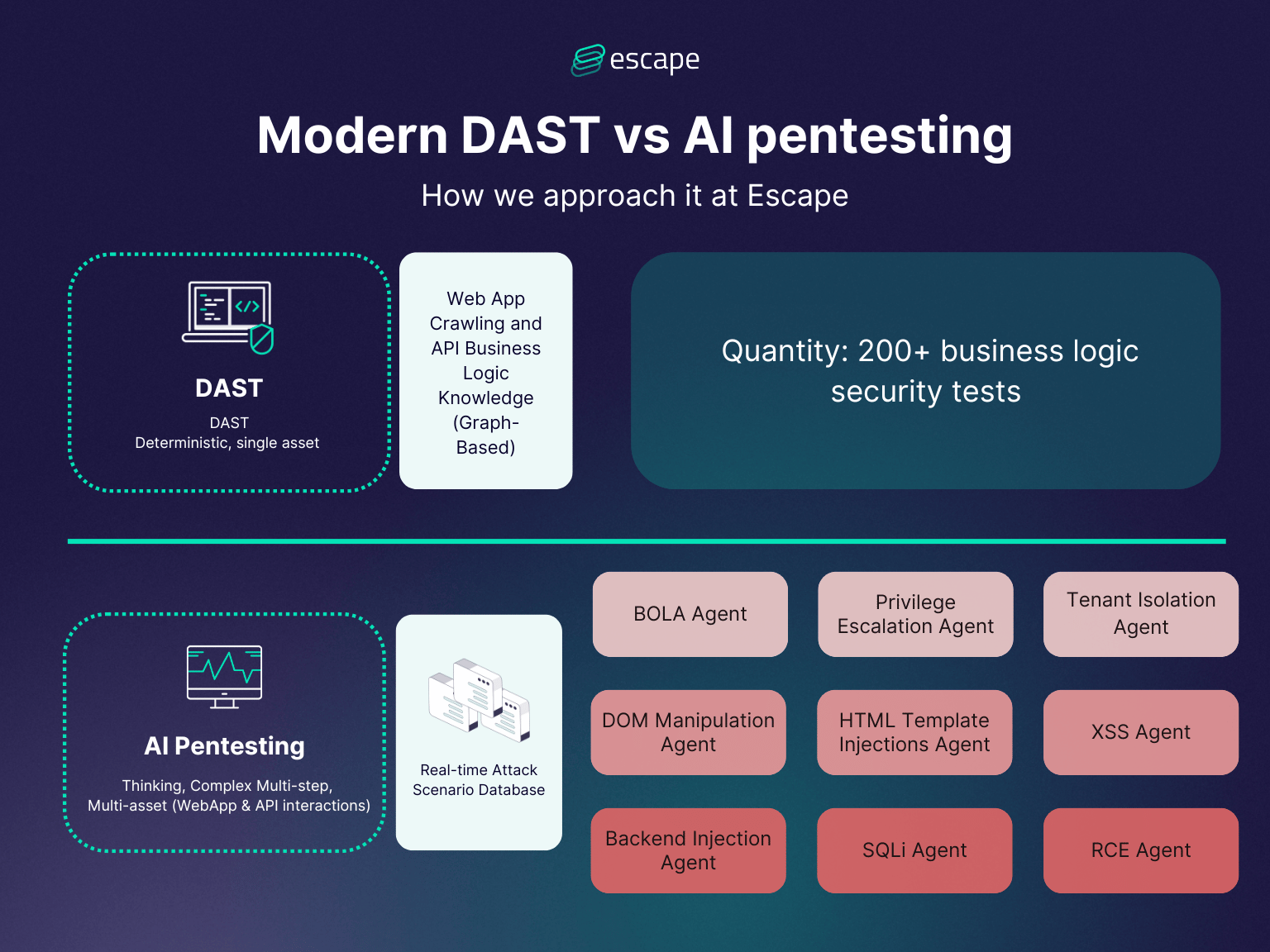
You can build a real, agentic offensive security solution. You allow thinking complex multi-step attack scenarios that can involve multiple assets. So it's not just targeting an API or targeting a web app. It targets attack chains and identifies those that may involve not only the web app but also API interactions.
This is the critical difference between DAST and pentesting in 2026.
3. The Power of Multi-Asset Attack Chains
To sum up, AI automated pentesting leverages the DAST foundation to discover attack chains that:
- Start at one API endpoint
- Pivot through a web application
- Exploit relationships between different assets
- Chain multiple vulnerabilities together
- Mirror real-world attacker behavior
Most organizations have hundreds of vulnerabilities. Only a handful represent realistic breach scenarios. AI pentesting can help identify attack paths that lead to them more precisely.
Agentic Pentesting: Specialized Mission-Focused Testing
Building on the DAST knowledge graph foundation, agentic penetration testing tools deploy specialized agents that might run in parallel with DAST testing but focus on specific offensive security missions.
BOLA (Broken Object Level Authorization) Agents
One of the most common BOLAs we hear security teams want tested is privilege escalation and tenant isolation.
Privilege Escalation Testing: Consider an organization with admin and member users. Obviously, members shouldn't have admin privileges, but how do you test this at scale across hundreds of endpoints?
BOLA agents:
- Ingest role-based access control (RBAC) matrices from your environment
- Infer what actions each role should and shouldn't perform
- Test privilege boundaries automatically
- Identify privilege escalation paths
Tenant Isolation Testing: For multi-tenant applications, ensuring one customer cannot access another's data is critical. BOLA agents systematically test isolation boundaries.
Why the Knowledge Graph Makes AI Pentesting Uniquely Powerful
This is worth emphasizing because it's the secret sauce that makes AI pentesting dramatically more effective than pure LLM-based approaches:
The DAST knowledge graph provides:
Strategic Focus:
- Agents focus on attack paths that matter based on your actual application architecture, not just test every theoretical attack
- This intelligence guides agents to high-value targets first
- The graph shows which endpoints are publicly exposed vs internal, which handle sensitive data, which are authentication-adjacent
Application Context:
- Testing is informed by deep understanding of how your application actually works
- Agents know which requests must be sequenced, which parameters are related, which endpoints share authentication contexts
- This dramatically reduces false positives and increases exploitation success rates
Efficient Exploitation:
- Rather than relying purely on LLM reasoning (which can be unfocused, inefficient, and prone to hallucination), agents use the graph to guide strategic attack planning
- The graph acts as a map showing paths between vulnerable components
- Agents can reason: 'If I compromise endpoint A, what downstream systems become accessible?'
This combination is fundamentally more powerful than:
❌ Pure agentic architectures (master agent + sub-agents without knowledge graphs)
- Lack strategic guidance
- Test randomly or based on generic patterns
- High false positive rates
- Miss attack chains that require application-specific knowledge
❌ Traditional DAST (even with AI-enhanced detection)
- Single-step testing only
- No attack chain discovery
- Pattern-matching without strategic thinking
- Can't reason about multi-asset scenarios
❌ Isolated AI scanning tools (without comprehensive application knowledge)
- Limited context about your environment
- Generic testing approaches
- Miss business logic specific to your application
- Can't validate findings with real exploitation
The combination of graph-based knowledge + AI-powered multi-step reasoning + specialized offensive agents = pentesting power at automated scale.
And this is what we do at Escape. If you want to learn more, schedule a call with our team.
DAST vs AI Penetration Testing: Quick Recap
| Modern DAST | AI-powered Pentesting | |
|---|---|---|
| Findings Type | • Static list of CWEs and CVEs | • Zero-days and complex multi-step business logic vulnerabilities |
| Testing Type | • 200+ single-step business logic security tests | • Multi-step, complex attack scenarios, Tests across multiple assets simultaneously • Identifies attack chains that span web apps and APIs |
| Depth | • High | • Very high |
| Additional Key Features |
• Easy CI/CD integration • Screenshots, API Attack Path Validation, and logs • Tailored remediations for developers |
• Full pentesting process coverage: from discovery to exploitation to remediation • Agentic reasoning on complex attack chains • Regression testing (ingest findings from bug bounty reports that the AI reproduces at scale to prevent recurrence) • Detailed compliance reporting |
| Scan Time | • Fast | • Medium |
| Scan Cost | • Low | • High |
| Usage | • DevSecOps / Continuous in CI/CD | • Can be implemented in CI/CD, but usually more periodic |
| Scan Stability / Results Consistency | • Perfect | • Medium |
Will Manual Pentesting Be Replaced by Automated Pentesting?
Let's address the elephant in the room: Can AI really replace skilled penetration testers?
Short answer: No.
Longer answer: It's not trying to.
The relationship between AI automated pentesting and manual pentesting isn't replacement, it's an evolution and specialization.
Manual pentesting has a fundamental math problem that technology has to solve:
The numbers:
- Average enterprise: 200+ applications
- Development velocity: 10+ deployments per day
- Pentest frequency: 1-4 times per year per application
- Pentest duration: 2-4 weeks per application
- Coverage gap: 99%+ of the time, your applications are untested
Automated pentesting is just the solution to this math problem to really escape the limits of manual pentesting.
The relationship between AI automated pentesting and manual pentesting is symbiotic:
Regression Testing: When manual pentesters or bug bounty programs discover vulnerabilities, AI automated pentesting can:
- Ingest findings from pentest reports
- Create automated tests to prevent recurrence
- Validate fixes in real-time
- Scale learnings across all applications
Continuous Validation: Rather than eliminating manual testing, AI automated pentesting:
- Handles routine, repetitive testing
- Frees pentesters to focus on complex scenarios
- Provides continuous coverage between manual assessments
- Enables "pentesting web-coded apps at scale".
Conclusion: Choosing Your Approach: DAST or Penetration Testing?
The question when it comes to comparison between DAST and penetration testing isn't which approach is "best". It's up to you to conclude which combination serves your organization's needs:
- DAST provides breadth and speed for known vulnerabilities
- Manual pentesting delivers depth and expertise for complex scenarios occasionally for highly critical applications
- AI automated pentesting bridges the gap, providing pentesting-level testing at DAST-level scale
Use Modern DAST When:
- You need business logic testing at scale, but single-step security tests are sufficient
- Compliance requires automated scanning
- Budget is more limited
- You need simple CI/CD integration
- You're building a foundation for future capabilities
Use AI Automated Pentesting When:
- You deploy continuously and need a matching security velocity
- You need multi-step attack scenario testing
- Attack chains across multiple assets concern you
- You want pentesting depth at the DAST scale
- Compliance mandates a penetration testing report
As development velocity accelerates and attack surfaces expand, organizations need security testing that can keep pace. AI-powered automated pentesting represents the evolution of both DAST and traditional pentesting, combining the scalability of automated tools with the depth and business logic understanding of human pentesters.
Looking to learn more about how modern automated pentesting differs from traditional DAST? Explore how platforms like Escape are redefining application security testing with AI-powered, graph-based pentesting at scale.
💡 Check out more relevant articles below:
